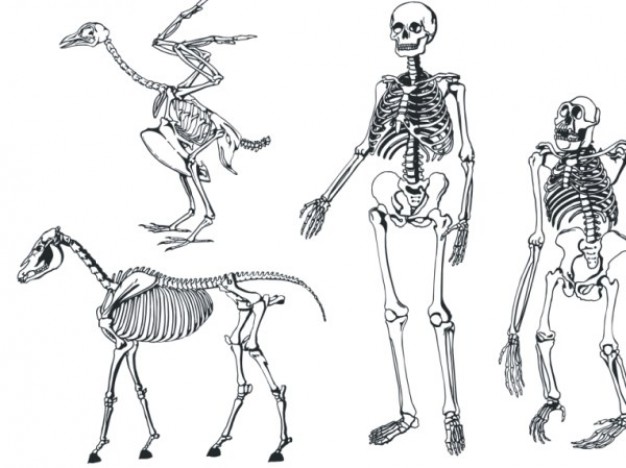
skeleton wiki:
>For other uses, see Skeleton (disambiguation). In biology, the skeleton or skeletal system is the biological system providing support in living organisms. (By extension, non-biological outline structures such as gantries or buildings may also acquire skeletons.)Skeletal systems are commonly divided into three types - external (an exoskeleton), internal (an endoskeleton), and fluid based (a hydrostatic skeleton), though hydrostatic skeletal systems may be classified separately from the other two since they lack hardened support structures. Large external skeletal systems support proportionally less weight than endoskeletons of the same size, and thus many larger animals, such as the vertebrates, have internal skeletal systems. Examples of exoskeletons are found in arthropods, shellfish, and some insects: the skeleton forms a hard shell-like covering protecting the internal organs.
See more at Wikipedia.org...
animal wiki:
>For the Muppet Show character, see Animal (Muppet). For the professional wrestler, see Joseph Laurinaitis. Porifera (sponges)Ctenophora (comb jellies)Cnidaria (coral, jellyfish, anenomes)Placozoa (trichoplax)Subregnum Bilateria (bilateral symmetry)Acoelomorpha (basal)Orthonectida (flatworms, echinoderms, etc.)Rhombozoa (dicyemids)Myxozoa (slime animals) Superphylum Deuterostomia (blastopore becomes anus)Chordata (vertebrates, etc.)Hemichordata (acorn worms)Echinodermata (starfish, urchins)Chaetognatha (arrow worms)Superphylum Ecdysozoa (shed exoskeleton)Kinorhyncha (mud dragons)LoriciferaPriapulida (priapulid worms)Nematoda (roundworms)Nematomorpha (horsehair worms)Onychophora (velvet worms)Tardigrada (water bears)Arthropoda (insects, etc.)Superphylum PlatyzoaPlatyhelminthes (flatworms)Gastrotricha (gastrotrichs)Rotifera (rotifers)Acanthocephala (acanthocephalans)Gnathostomulida (jaw worms)Micrognathozoa (limnognathia)Cycliophora (pandora)Superphylum Lophotrochozoa (trochophore larvae / lophophores)Sipuncula (peanut worms)Nemertea (ribbon worms)Phoronida (horseshoe worms)Ectoprocta (moss animals)Entoprocta (goblet worms)Brachiopoda (brachipods)Mollusca (mollusks)Annelida (segmented worms) Animals are a major group of organisms, classified as the kingdom Animalia or Metazoa. In general they are multicellular, capable of locomotion and responsive to their environment, and feed by consuming other organisms. Their body plan becomes fixed as they develop, usually early on in their development as embryos, although some undergo a process of metamorphosis later on. Human beings are classified as members of the animal kingdom.
See more at Wikipedia.org...
Human wiki:
o%20sapiens%20cromagnon">Homo sapiens cromagnon (extinct) Homo sapiens idaltu (extinct) Homo sapiens sapiens For other uses, see Human (disambiguation). Humans or human beings define themselves in biological, social, and spiritual terms. Biologically, humans are classified as the species Homo sapiens (Latin for "thinking man"): a bipedal primate of the superfamily Hominoidea, together with the other apes: chimpanzees, gorillas, orangutans, and gibbons.
See more at Wikipedia.org...